mango gi index
The gi index is an indicator that measures the speed of absorption of food containing carbohydrates into the body and the speed at which it raises blood sugar.
The food component is given a number from 0 to 100, meaning the higher the number, the higher the increase in insulin and the greater its harm.
Fast carbohydrates are carbohydrates that your body absorbs quickly, such as white sugar, flour, pastry, bread …. etc
These fast carbohydrates increase the fast activity of the hormone insulin in the blood
When this hormone rises in the body, it enters the body in its building and storing stage of fats.
The more you keep this hormone low, the more fat you will burn, build a healthier body, and lose weight.
To keep the insulin hormone low, this directly depends on the type of food you eat and primarily the carbohydrates.
And since mangoes contain natural sugar, you are probably wondering if mangoes are right for your diet.
In this article, we will explain whether you can safely eat this fruit in your diet, or if it is so dangerous that we will stay away from it.

The nutritional value of mangoes
Mango ranks as one of the most nutritious fruits.
It provides the body with calories, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and its peel, seeds, and core contain many bioactive compounds, which include food and non-food compounds that have biological properties that work through oxidation and reduction mechanisms.
Mango is one of the most famous fruits in the world, and it has many potential benefits, and it belongs to a family called the Drupe family, which is one of the plants that have a soft and thick pulp that surrounds a cavity that contains the seed.
These are some of the nutrients found in 100 grams of mango:
- Calories 60 calories
- Water is 83.46 ml
- Protein 0.82 grams
- Fat 0.38 grams
- Carbohydrates 14.98 grams
- Fiber: 1.6 grams
- Sugar 13.66 grams
- Calcium 11 mg
- Iron is 0.16 mg
- Magnesium 10 mg
- Phosphorous 14 mg
- Potassium 168 milligrams
- Sodium 1 mg
- Vitamin C 36.4 mg
- Vitamin A 1082 International Units
- Folate 43 micrograms
100 grams of mango covers about 70% of our daily needs for most of the previous elements, and this indicates the value of this fruit for being very nutritious for almost any diet.

How does mango affect blood sugar (mango gi index)?
The reason for the presence of this amount of calories is sugar, which makes the sugars of this fruit have a negative effect on blood sugar, that is, they contribute to increased blood sugar in diabetics.
However, eating mango does not mean eating sugars only! Rather, eating fiber and various antioxidants, which play an important role in reducing the effect of this amount of sugar in the blood.
Fibers are able to slow down the rate at which your body absorbs sugar, which lowers the glycemic index number, which we previously mentioned measures how quickly our bodies absorb sugar.
Not only that, but the antioxidants work to reduce any stress response associated with high blood sugar levels.
Thus, the effect of mango on blood sugar is not as dangerous as some would expect, but rather the opposite as it is very safe for any system focused on improving blood sugar.
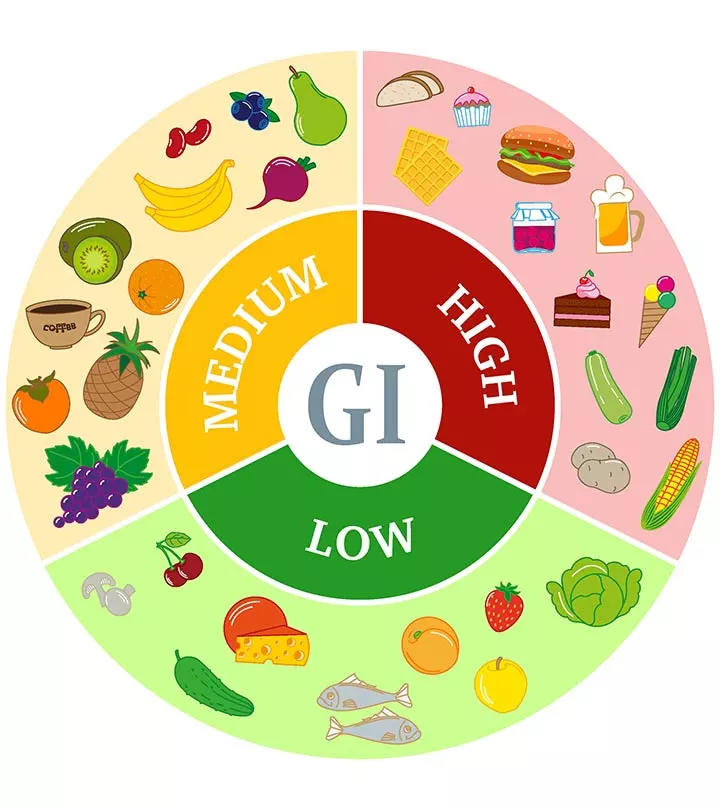
As we have previously mentioned, the gi index is a measure of how quickly our bodies absorb sugar, and therefore it is a tool used to classify foods according to their effect on blood sugar. mango gi index
Hence, in order to measure this process and the energy that the body needs to absorb food, a standard science called the gi index has emerged, and here all foods were presented for the measurement process.
There are a variety of research methods for assessing how the glycemic index evaluates food. In general, this number depends on the amount of food that raises blood glucose levels in the healthy people who participated in the research compared to the amount of pure glucose that raised their blood glucose level. The glycemic index values are usually divided into three categories:
Low glycemic index: 1 to 55
Average glycemic index: 56 to 69
High glycemic index: 70 or more
After the mango was introduced for the measurement process, it was found that the mango gi index 51, which classifies it as a low-glycemic index food.
However, it is no secret to you that people’s physiological responses to food differ, and therefore if we consider that mango is a healthy choice of carbohydrates, this does not mean that it is for you, and therefore you must personally evaluate your response to it to determine the amount that you should include in your diet.
How to make mango more diabetic friendly
If you have diabetes and want to include mangoes in your diet, we have strategies to reduce the likelihood of an increase in blood sugar.
The best way to reduce the blood sugar effects of this fruit is to avoid eating too much at once.
If you have diabetes, you can test yourself by eating 80 grams of mangoes to see how your blood sugar responds.
Adding fiber to mangoes is a very suitable option to reduce blood sugar, and in the case of adding protein to mangoes, they are like a lot of fiber, helping to slow down the speed of digestion of sugars and thus reduce blood sugar.
Therefore, eating fruit on its own increases the likelihood of increased blood sugar than if you ate it after adding protein to it.
Try combining a mango with a marketed egg, a piece of cheese, or a handful of nuts in one meal, and you’ll be impressed with the results.
Mangoes and obesity
The purpose of the glycemic index diet is to eat foods that contain carbohydrates that are less likely to cause significant increases in blood sugar levels. This diet means losing weight and avoiding obesity-related chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
As mentioned earlier, the mango gi index, estimated at 51, does not indicate risk in terms of increased blood sugar, but on the contrary, a laboratory study published in Medicine in 2019 showed that mangoes may help reduce the risk of developing diabetes. , By reducing levels of sugar and fats in the blood, and contributing to the reduction of excess weight, because they contain mangiferin, and some phytochemical compounds, such as phenol, and flavonoid, And a study published in Nutrition and Metabolic Insights in 2014 showed that regular freezing and dried mangoes by obese people positively affected their fasting blood sugar levels, without negatively affecting weight.






